Tailored Custom Machine Guarding
Manufacturing Industries Served
Upgrade Your Equipment with Safety Guarding
Machine Safety for Film Packaging Equipment
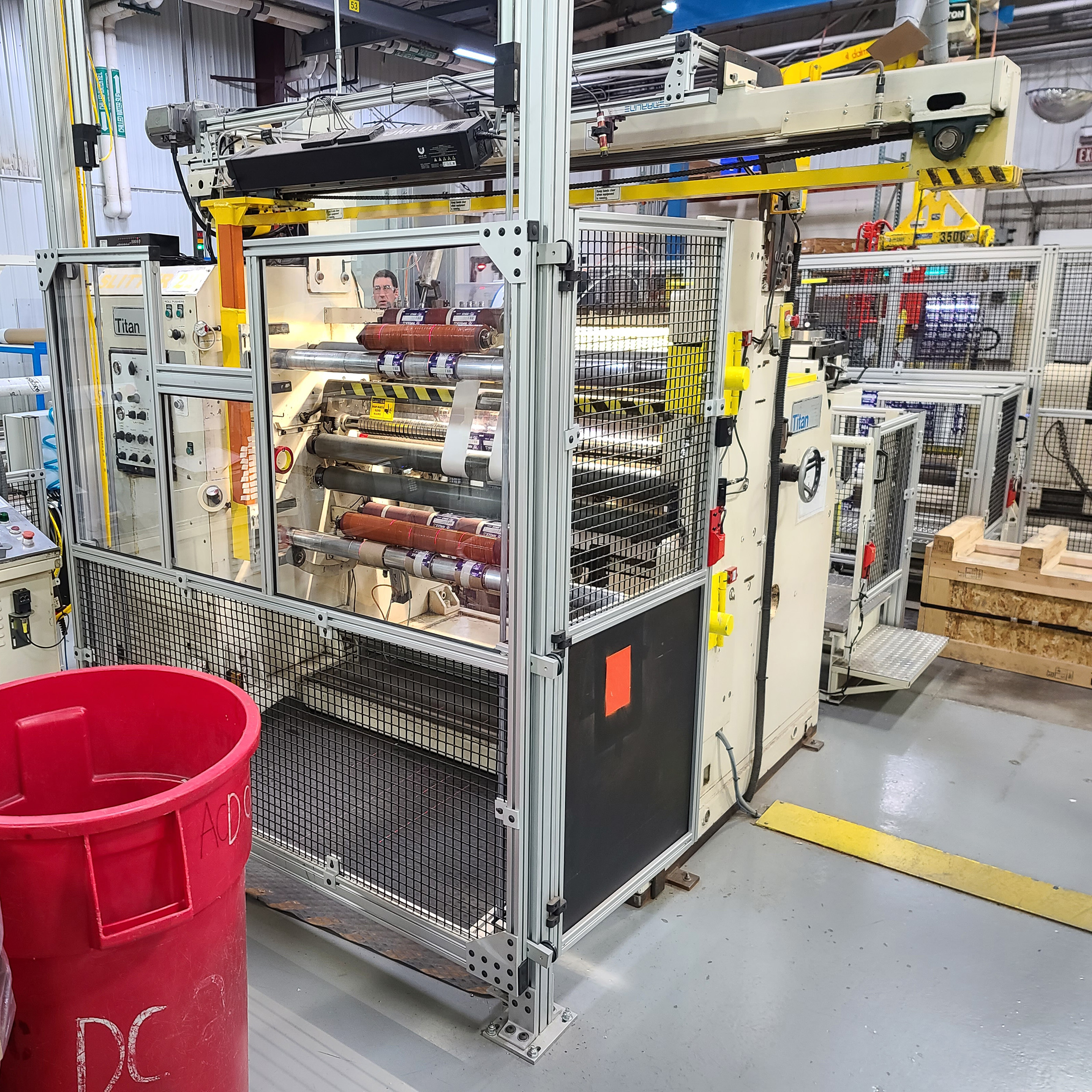

Familiar with the consumer goods film-based packaging industry, we can create machine safety solutions for numerous types.
These converting and web handling machines consist of:
- Slitters, doctors, rewinders, turret unwinders and rewinders, continuous winders, duplex slitters with rewinders, flame laminators, and cold nip roll coater.
The wide range of solutions include:
- Machine guarding with polycarbonate, safety switches, safety laser scanners, enabling switches with emergency stop, and pneumatic controls with location sensors.
All guards are designed and built to custom fit your specific application and operational methodologies, while being user-friendly providing a safer work environment.
Hazards to be mitigated with this type of guarding can include:
- Wrap points, in-running nip points, cut points, and crush points.
Corrugated Box Manufacturing Machine Safety
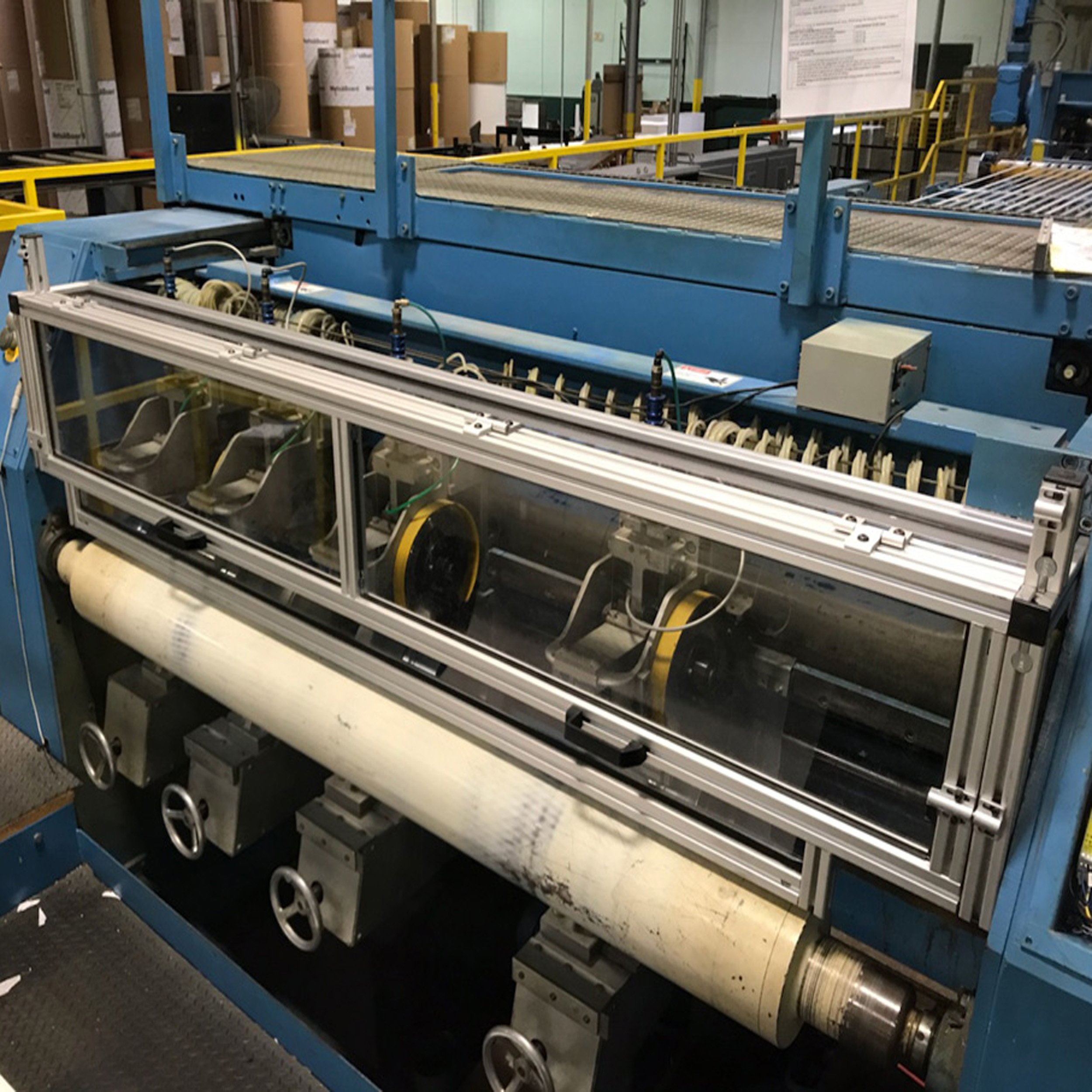

Experienced in the consumer goods corrugated-based packaging industry, we can create safety guarding solutions for various types regardless of where the converting is being done.
Paper and pulp or corrugated manufacturing equipment such as:
- In the wet mill with separators, evaporators, wet lap, and splitters
- Or in the paper mill with formers, slitters, rollers, and printers.
The wide range of solutions include:
- Various types of machine guards including nip guards, intrinsically-safe safety switches, laser scanners, dead man enabling switches, and air-operated controls.
Hazards to be mitigated with this type of guarding can include:
- Crush and cut points, wrapping points, and in-running nips.
Safeties for Industrial Motion Machines
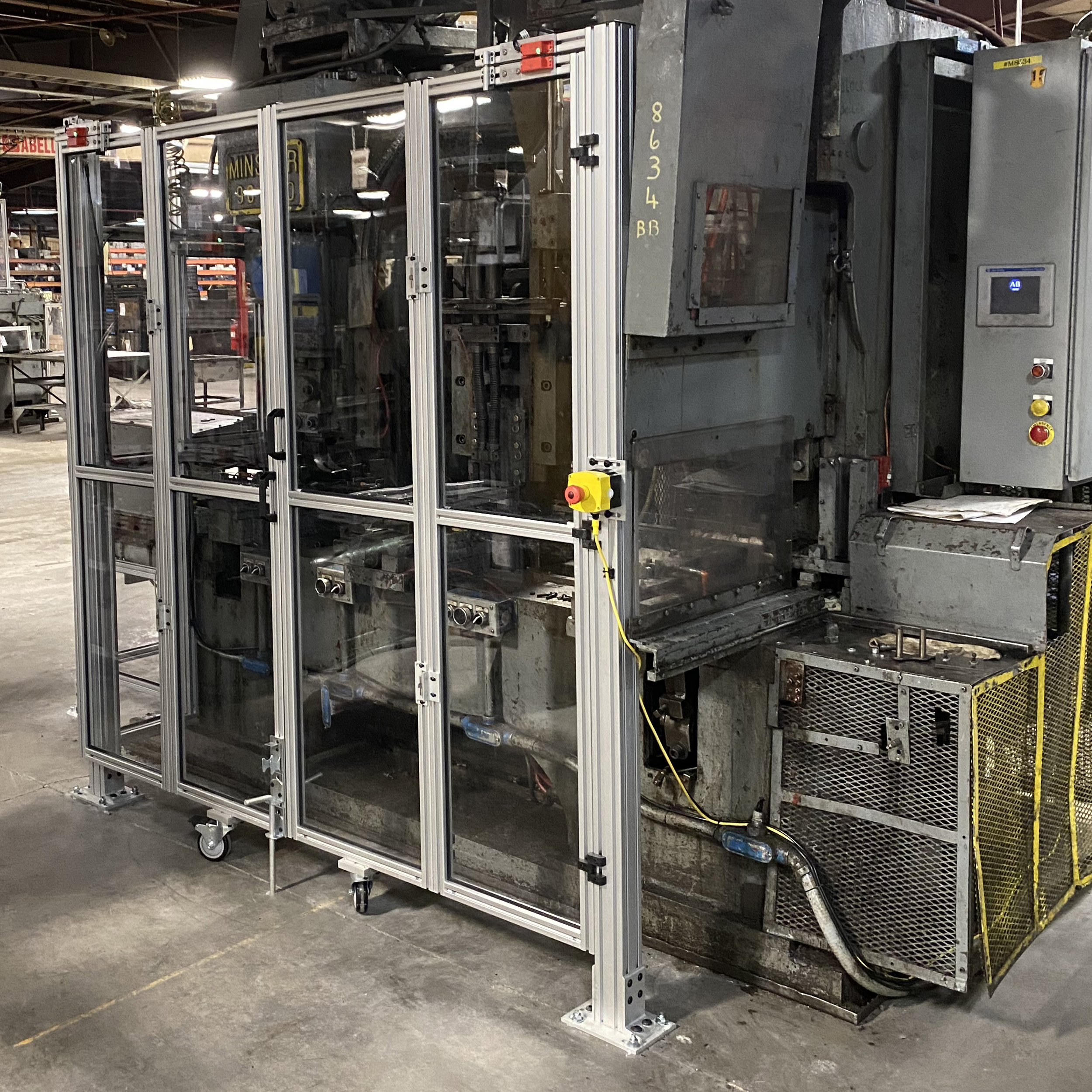

Industrial motion machines are used to manufacturer mechanical components such as:
- End shaft and take-up bearings, gears and sprockets, couplers, linear actuators, air and hydraulic cylinders, motors and pumps, and power transmission systems
Machines not manufactured with safety in mind requiring some level of human interaction or built as a semi-automated machine would include:
- Planers, hobbers, shapers, milling machines, broaches, flame hardening, and lathes
While these machines pre-date OSHA, they require industrial machine guarding with a level of administrative controls due to the human-interaction required for manual machining operations.
Machine guarding measures that can be used would be:
- Perimeter guarding, locking safety switches with speed monitoring, pneumatic and hydraulic safety valves, 2-hand controls, and CNC spin windows for viewability.
While a 100% safe environment may not be achievable, a safeR environment can be achieved my mitigating some hazards hazards:
- Entanglement, crush points drawing in, and trapping hazards.
Machine Safety for Wire and Cable Machines
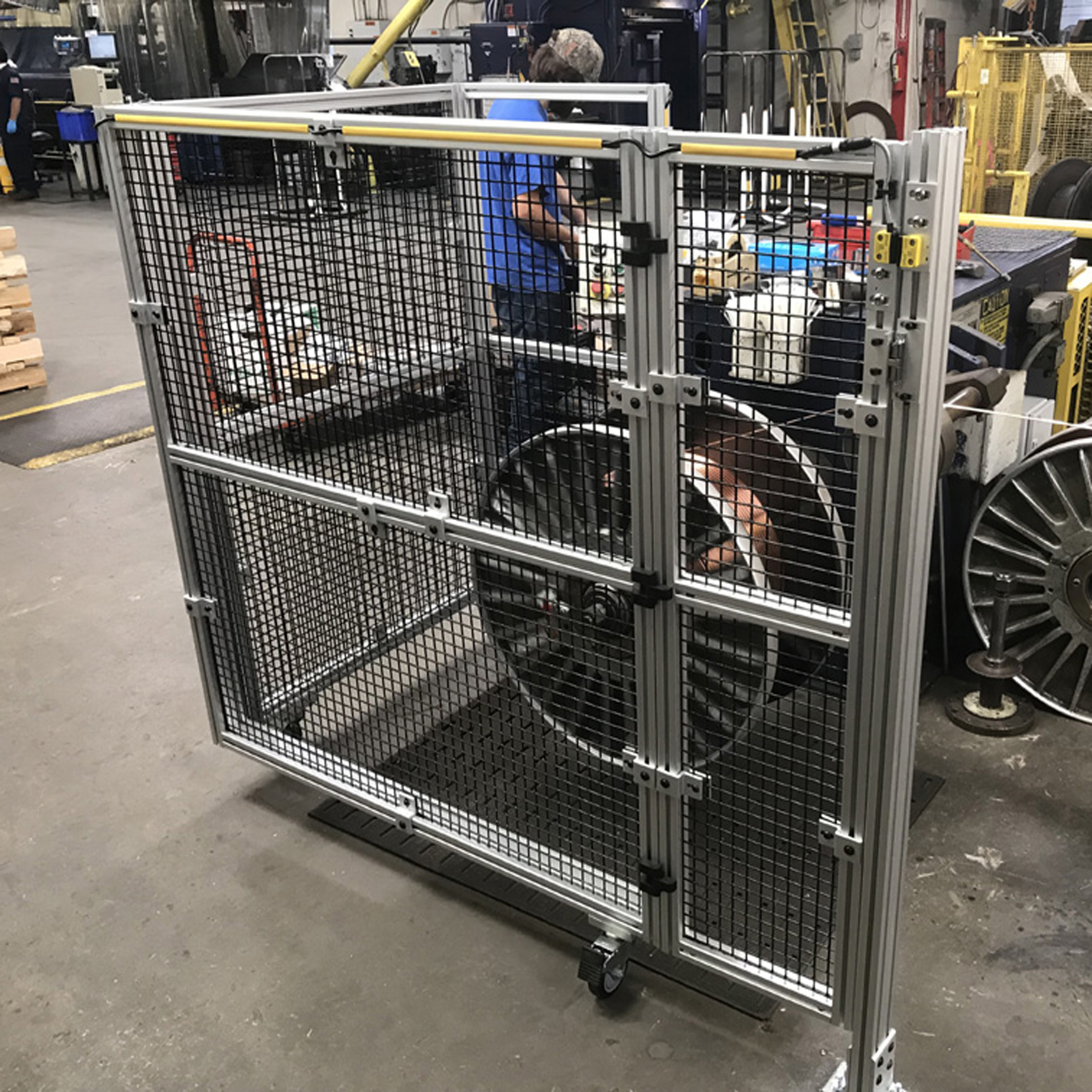

The production of insulated electrical wires and cables used for power transmission and communication present many inherent hazards through the machinery required to form, cut, and coil the materials for their intended use.
Machines produced before OSHA not focused on machine safety for operator protection:
- Extruders, SAMS or armoring machines, drawing equipment, strand machines, and cutting / winding machines.
Safety systems for these types of equipment could include:
- Steel guarding, zero-speed safety interlock switches, ballistic guards, protective bollards and guardrails, and safety light curtains.
These measures can reduced exposed hazards such as:
- Ergonomic issues, crushing points, friction and abrasion, entangled point, and tripping points.
Machine Safety in Insulation Manufacturing
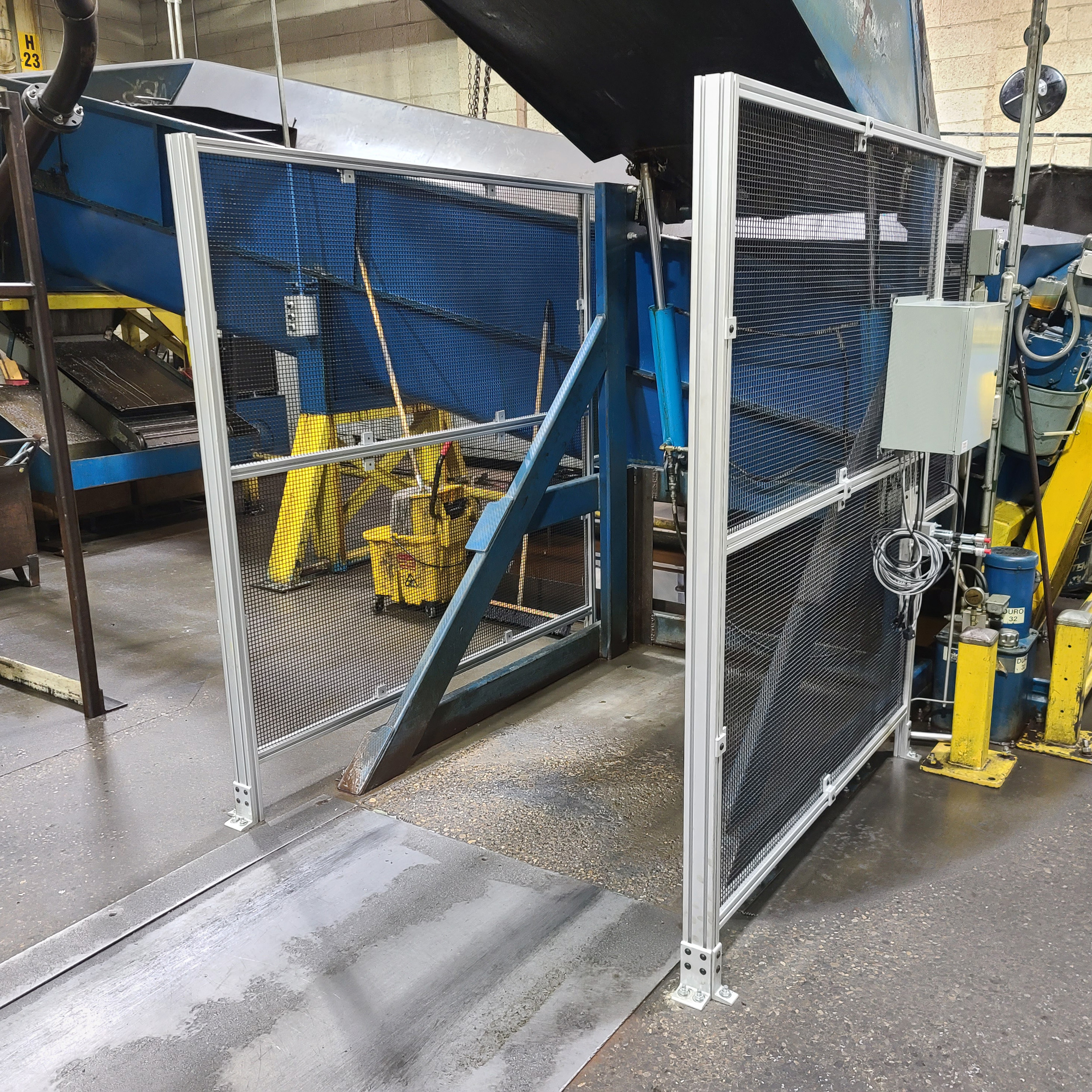

Manufacturing areas in large production facilities include the following machines or areas:
- Furnaces, spinner decks, and forming equipment are all parts of the hot end of producing fiber insulation. Whereas saws, slitters, choppers, facing pits, and miles of conveyors are found on the cold end of the manufacturing facility.
Creative solutions for each area in a large production facility is critical to the uptime of the equipment without requiring lockout / tagout (LOTO) or create emergency stop conditions.
These solutions can include air knives, no-touch tools, regulatory mesh openings, presence sensing devices including those susceptible to dirt, dust, and water, coupled with accessible emergency stop location for added protection.
Machine guarding commonly used in these types of facilities:
- Power transmission covers and guards, 3D safety radar systems, emergency rope pulls, safety guarding, trapped key interlocks, and safety mats.
Without proper machine guarding, countless hazards present themselves such as:
- Noise pollution, crushing and cut points, trapping and entanglement areas, puncture and pinch points.
Safety for Construction Product Manufacturing
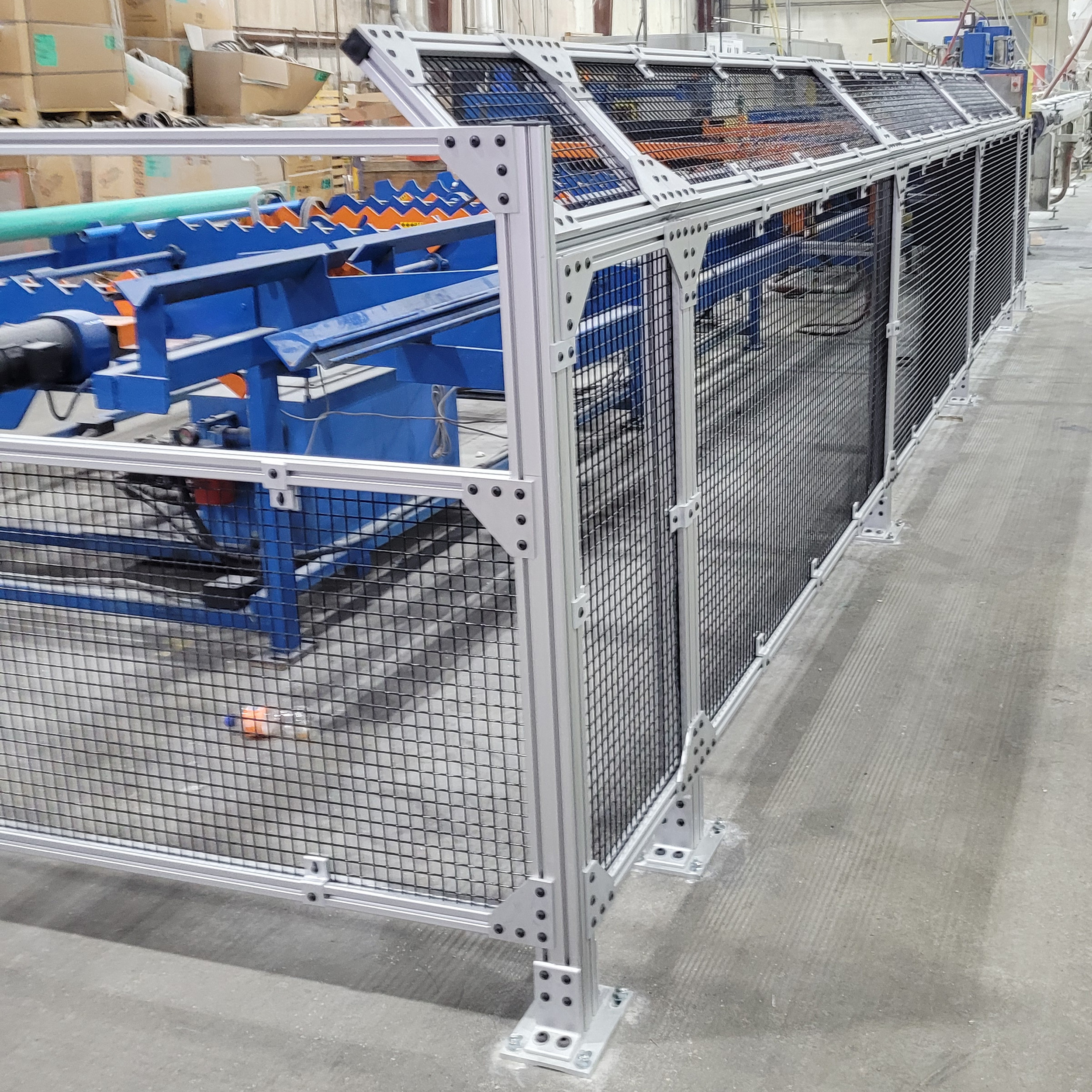

Continuous line production machines require a strategic approach to machine guarding to keep machines running while protecting operators at the same time.
Some of the machines that are factored into this engineered approach are:
- Barrel dies, upcut saws, extruders and formers, flippers, banding and strapping machines, as well as drawing and straightening equipment
Machine safety requires more than just physical guarding, which include:
- Perimeter guarding with protective posts, hood-style point guarding, area laser scanners, and non-locking safety switches.
Without proper machine guarding, countless hazards present themselves such as:
- Electrical shock, burns, ergonomics, striking from ejected materials, and shear points.
Metal Forming Machine Safety Guarding
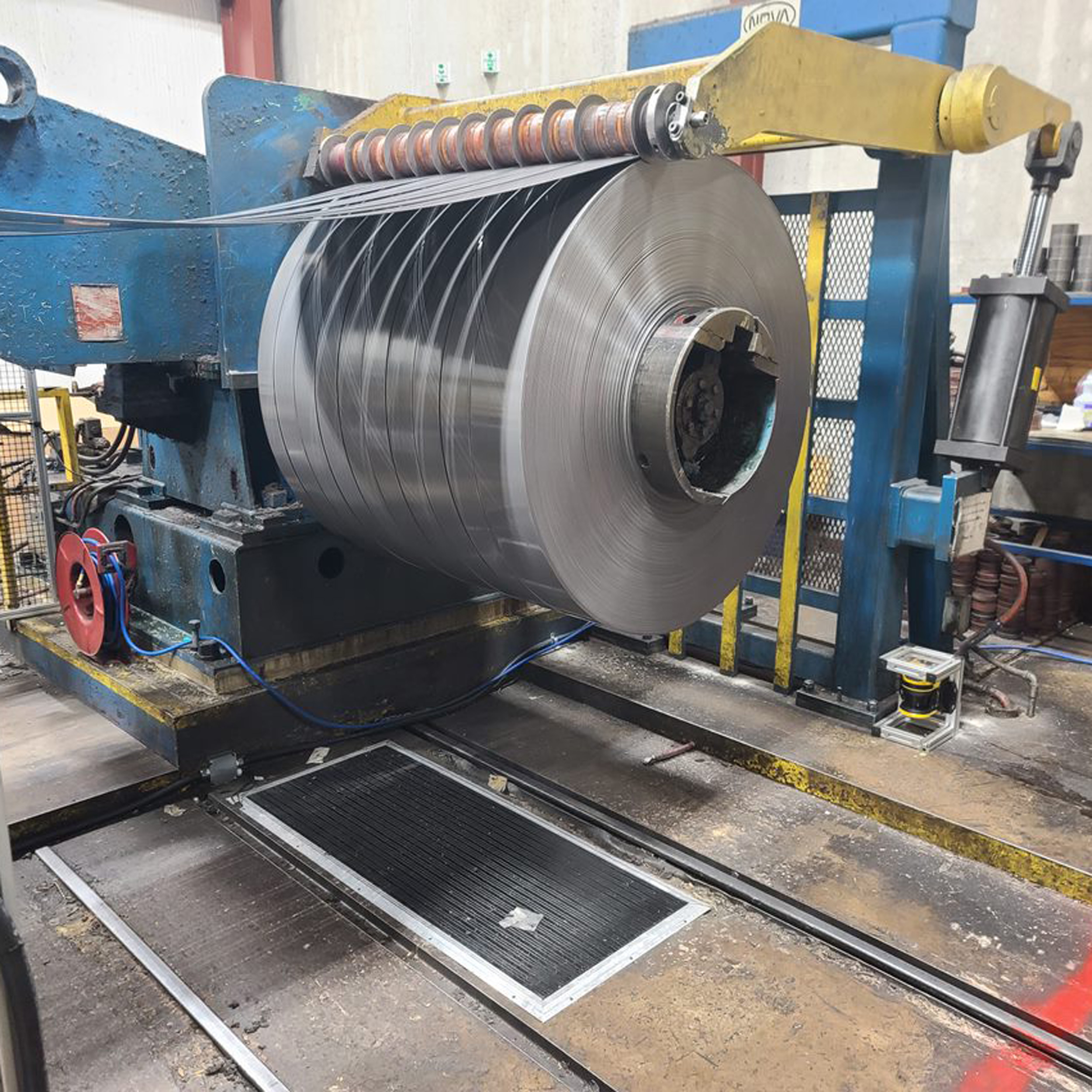

An age-old industry of hardworking mill, foundry, and casting workers is now requiring another level of protection. As the old-school workers transition out and the new-school transition in, the traditional "industrial revolution" methods, which are still relevant in metal forming, cannot be treated as an artform, rather an operation requiring greater protection.
- Units such as dumpers, hoppers and tippers to be guarded preventing crush, pinch, or shear operator injuries through use of safety laser scanners, photos eyes, hydraulic safety valves, and safety fencing.
- Unique safety measures for die cast machines, sand mixers, molding equipment, conveyors, robot packaging cells, and more. Solutions consisting of physical machine guarding, electronic safety devices, or a combination of both while focusing on operational support devices.
- Steel production transportation hazards such as crush and nip points can be minimized through the use of stack indicator lights, safety mats, and safety laser scanners, while still leaving access for PITs and overhead cranes.
- Machines such as payoffs or uncoilers, take-ups or recoilers, forming and sizing tube mills, h-coils or accumulators, and coil slitters designed to use safety fencing, laser scanners, and metal top safety mats to mitigate hazardous conditions.
Machine Enclosures for Food and Beverage
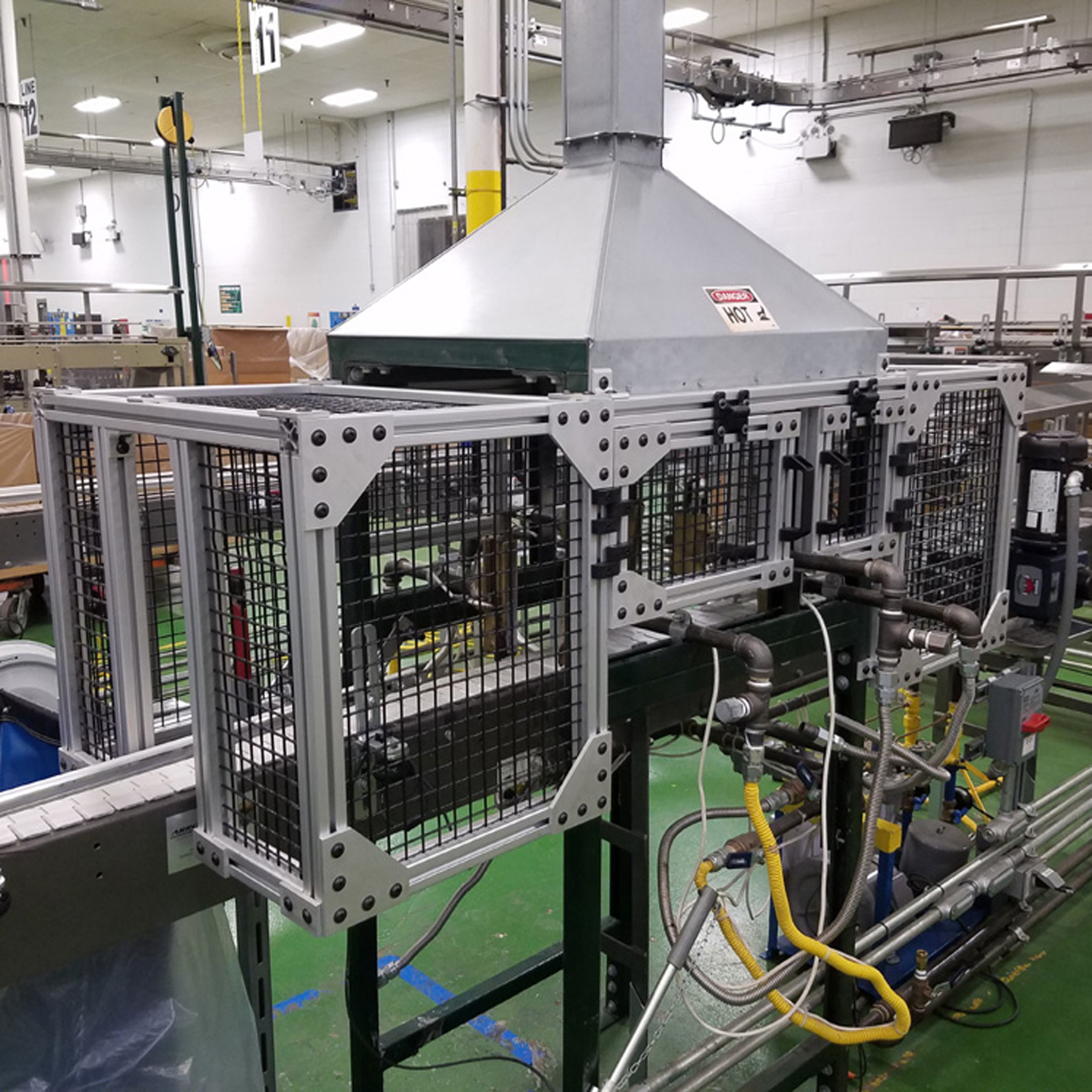

Production machines and isolated equipment found in the consumer products factories such as bottling and canning take a unique approach to safety guarding in order to protect the environment, including workers and machines.
Some of the machines that are factored into this engineered approach are:
- Cappers, labelers, indexers, flame treaters, orienters, plastic chain conveyors, blow molding and injection molding machines, and stamping equipment.
Machine safety requires more than just physical guarding, which include:
- Point of operation guarding with wire mesh and polycarbonate, rotating shaft guards, safety light curtains, and in some cases intrinsic safety or HazLoc safety.
Without proper machine guarding, countless hazards present themselves such as:
- Explosions, crush points, pinch and wrap points, burns, and entanglements.
Warehouse and Packaging Guards
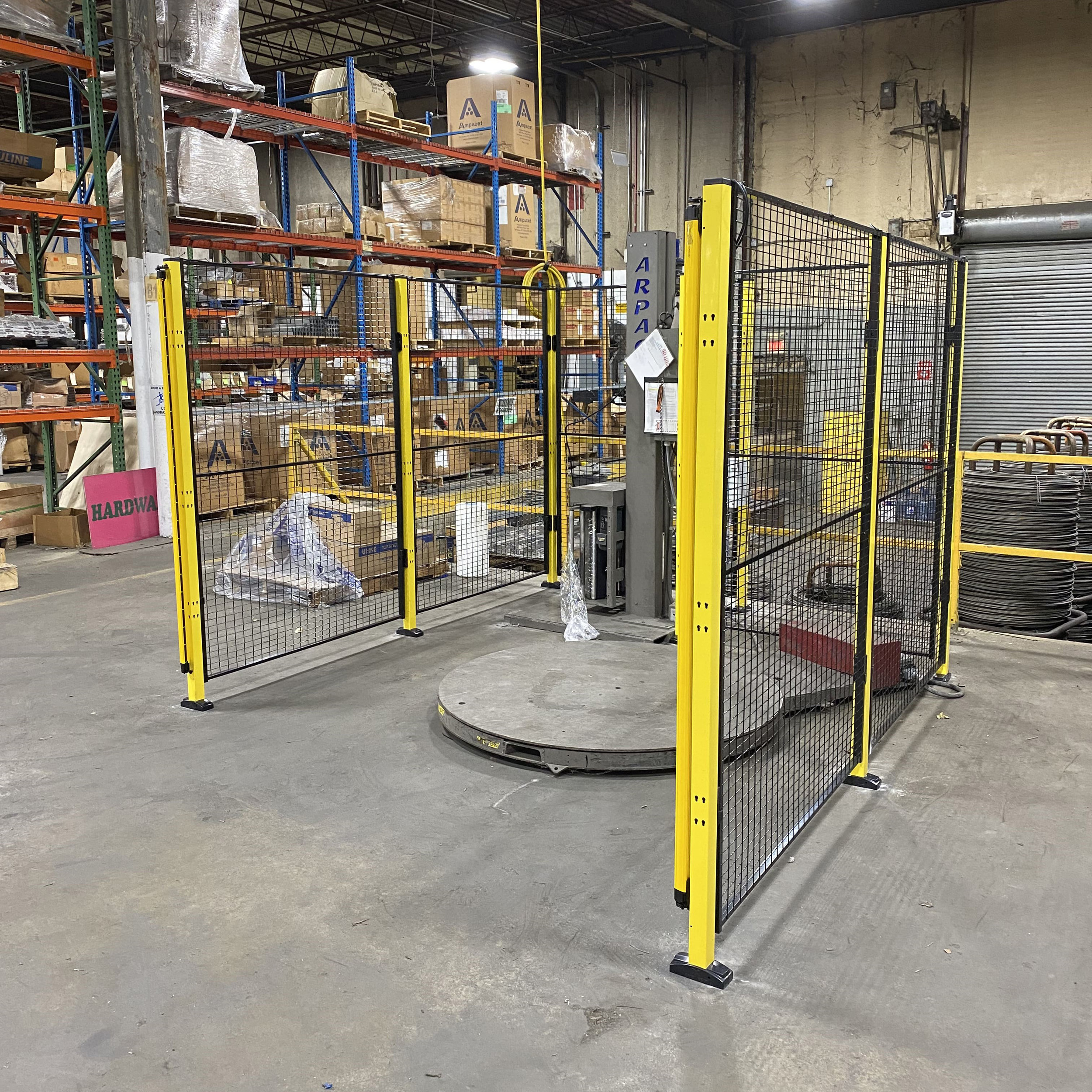

Palletizing systems, wrapping machines, dumpers and tippers, and conveyors are all active parts of the packaging industry, all requiring a level of safety based on accessibility.
Engineered for quick access, yet semi-simple solutions to guard the machines while working around packaging materials like pallets and skids would be:
- Perimeter guarding with mesh, safety scanners, light curtains or light bars, guarding for couplings, idler rollers, and chain drives.
Present hazards to overcome when providing a safer environment:
- Trip hazards, wrap points, in-running nips, impact points, and crushing points.
Aggregate and Mining Machine Safety
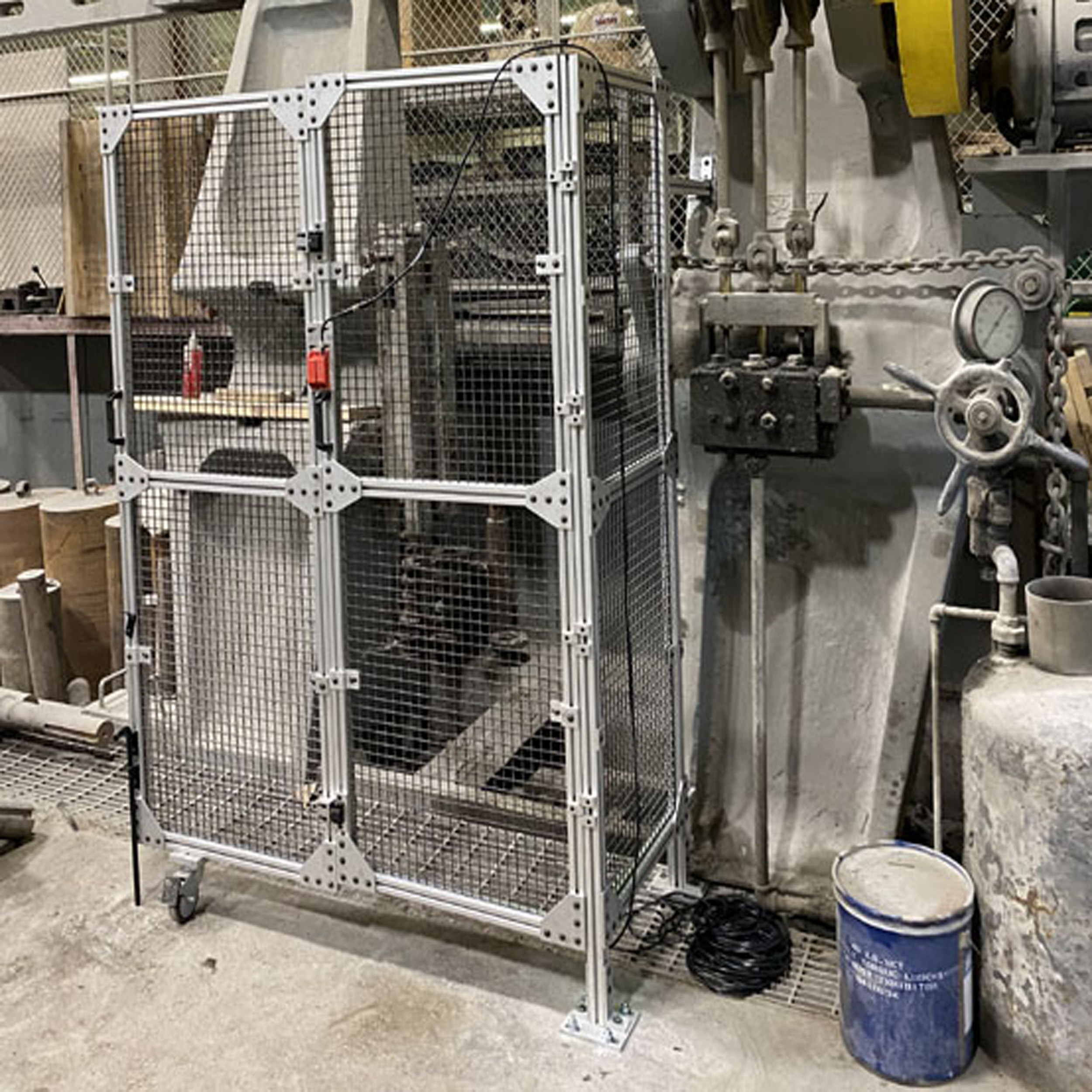

With our installation crew MSHA-24 certified, we can assist with safety solutions for mining tools, as well as for the maintenance equipment used to keep these machines actively running.
Mining equipment along with the maintenance machines for repairs would be:
- Crushers, feeders, conveyors, screens and shakers, and wheel loaders.
- Mills, lathes, drill presses, shop presses, bandsaws, buffers and grinders.
Machine guarding needed for these types of machines:
- Steel guarding, industrial interlock safety switches, power transmission covers, point guarding, adjustable tooling guards with safety switches, and protective shields.
These measures can reduced exposed hazards such as:
- Ergonomic issues, crushing points, friction and abrasion, entangled point, and tripping points.
Tunnel Guarding for EV Battery Production Line

Perimeter tunnels designed, manufactured, and installed to protect batteries, streamline production, and support compliance.
We provide turnkey tunnel-guarding systems for electric-vehicle (EV) battery production lines. Our solutions use T-slot aluminum, clear polycarbonate, and a wide range of accessories for fast, seamless installation that helps reduce risk and maintain throughput. For more details, visit our blog or our Knowledge Hub for a complete design guide made to your application.
AG or Agriculture Machine Safety Solutions

The AG industry is a tough environment both indoors and outdoors, providing unique solutions to mitigate hazardous conditions. for cage mills and pulverizers covering rotating shafts and exposed bearings, protective solutions for driven and non-driven rollers on conveyors, as well as guarding for the machine shop equipment in the maintenance department..
Machines actively found in the AG industry consist of:
- Cage mills, pulverizers, shakers, presses, kilns, and splitters.
- Exposed bearings, motor and pump shafts, and chain and belt drives can be found throughout the miles of conveyor systems and tank farms.
- Maintenance equipment pertaining to drills, mills, lathes, grinders, and buffers.
Safety systems for these types of equipment could include:
- Steel guarding, zero-speed safety interlock switches, ballistic guards, protective bollards and guardrails, and safety light curtains.
These measures can reduced exposed hazards such as:
- Ergonomic exposure, crushing points, abrasion and friction burns, entanglement areas, pinch points, and tripping points.