Presence Sensing Safety Devices
Safety Laser Scanners
Advanced industrial safeguarding with the KEYENCE Safety Laser Scanner
Customize detection zones and safeguard operators with the KEYENCE Safety Laser Scanner – compact, network-ready, and highly reliable.
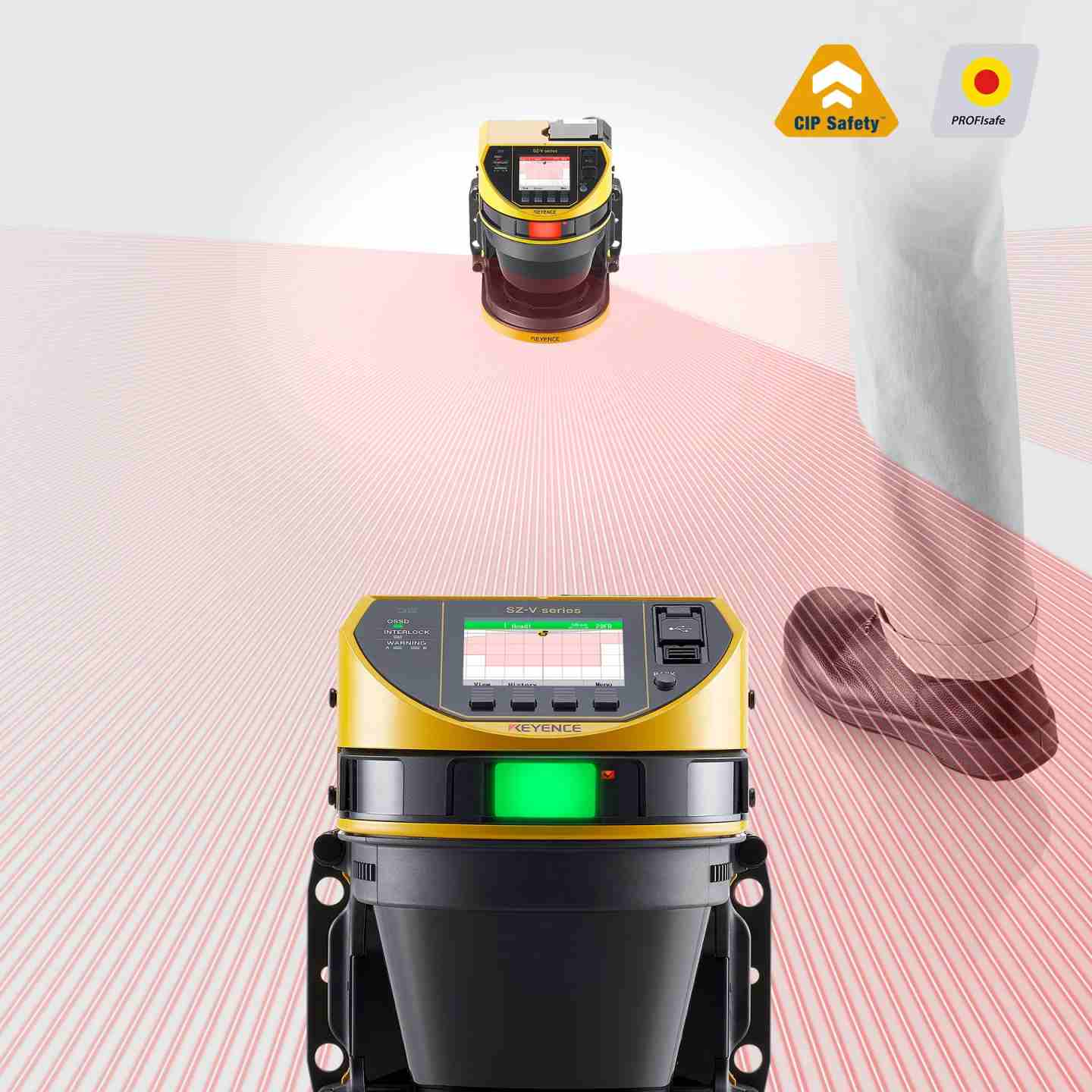
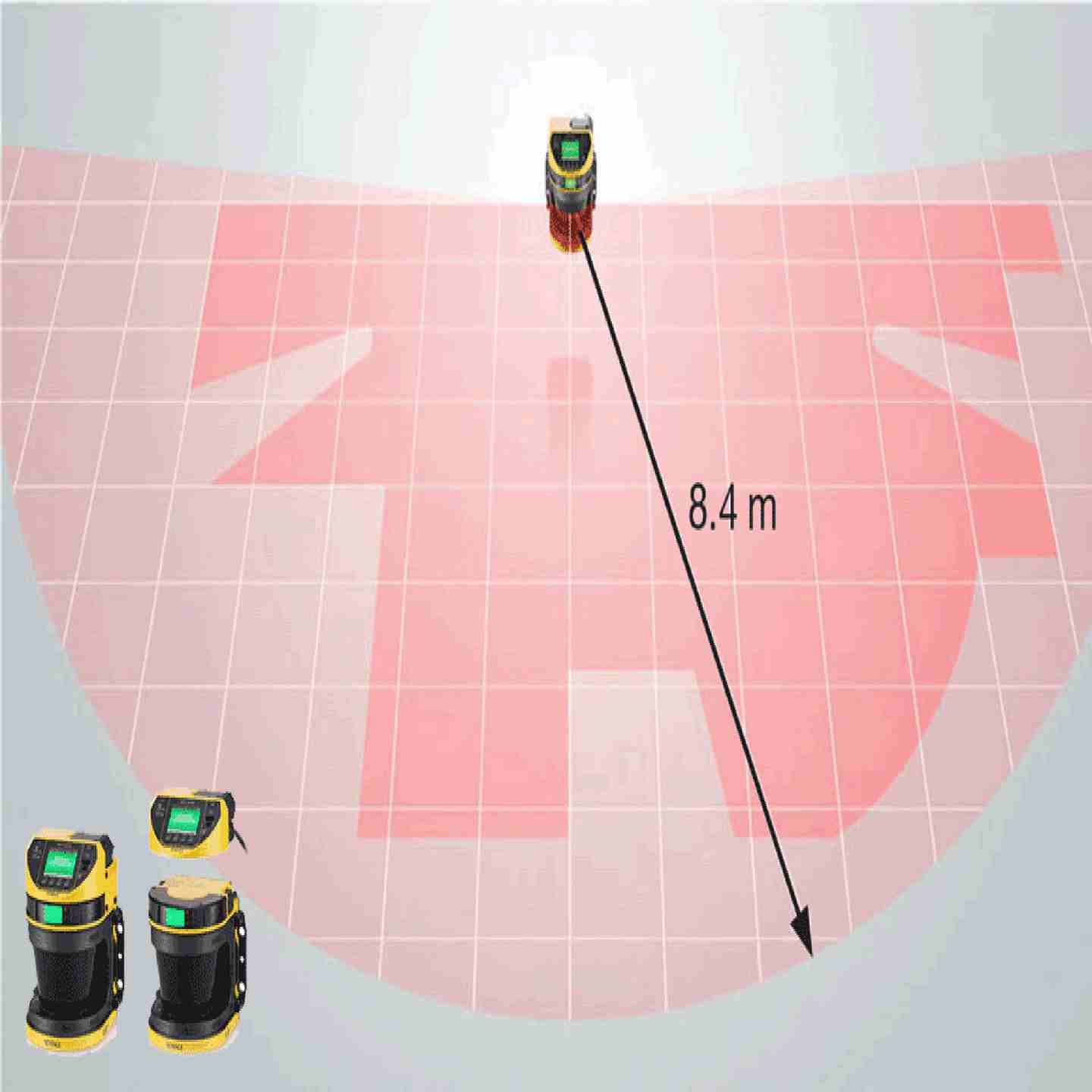
A Safety Laser Scanner is a high-precision, safety-rated sensing device that uses advanced laser technology to detect people or objects within a defined protection zone around industrial machines. Designed for flexible safeguarding, it creates configurable 2D detection fields that automatically stop hazardous motion when a person enters the area. Keyence laser scanners are widely used in manufacturing for perimeter guarding, mobile robot safety, and access prevention, offering fast response times, easy setup, and reliable compliance with OSHA/ANSI/ISO machine safety standards.
User-Friendly Design
- Intuitive configuration software enables rapid zone setup in minutes.
- Compact footprint ideal for crowded or variable process areas.
- Integrated diagnostics and status indicators simplify service and monitoring.
Flexible Mounting Options
- Suitable for horizontal or vertical installation, enabling area-protection or access-protection applications.
- Configurable protection zones shaped freely to accommodate complex layouts.
- Robust environmental ratings (dust/debris resistance) support harsh manufacturing environments.
Seamless System Integration
- Certified to meet IEC 61496 Type 3, SIL 2, ISO 13849 PLd/Category 3 standards.
- Network-capable models support CIP Safety, PROFINET/PROFIsafe and remote monitoring.
- Multi-bank zone switching and cascading features reduce wiring and simplify safety system layout.
Safety Laser Scanners
Advanced industrial safeguarding with the KEYENCE Safety Laser Scanner
Customize detection zones and safeguard operators with the KEYENCE Safety Laser Scanner – compact, network-ready, and highly reliable.
A Safety Laser Scanner is a high-precision, safety-rated sensing device that uses advanced laser technology to detect people or objects within a defined protection zone around industrial machines. Designed for flexible safeguarding, it creates configurable 2D detection fields that automatically stop hazardous motion when a person enters the area. Keyence laser scanners are widely used in manufacturing for perimeter guarding, mobile robot safety, and access prevention, offering fast response times, easy setup, and reliable compliance with OSHA/ANSI/ISO machine safety standards.
User-Friendly Design
- Intuitive configuration software enables rapid zone setup in minutes.
- Compact footprint ideal for crowded or variable process areas.
- Integrated diagnostics and status indicators simplify service and monitoring.
Flexible Mounting Options
- Suitable for horizontal or vertical installation, enabling area-protection or access-protection applications.
- Configurable protection zones shaped freely to accommodate complex layouts.
- Robust environmental ratings (dust/debris resistance) support harsh manufacturing environments.
Seamless System Integration
- Certified to meet IEC 61496 Type 3, SIL 2, ISO 13849 PLd/Category 3 standards.
- Network-capable models support CIP Safety, PROFINET/PROFIsafe and remote monitoring.
- Multi-bank zone switching and cascading features reduce wiring and simplify safety system layout.
- Assembly consists of:
- Scanner main unit (KEYENCE safety laser scanner).
- Mounting bracket kit and hardware for floor or wall application.
- Quick-start configuration software and user guide (digital).
- Power/I/O cable (e.g., 24 VDC input, OSSD outputs) — controller/safety relay sold separately.
- Common uses include:
- Area protection around robotic cells, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and dynamic machine zones.
- Access protection at doorways, removable guards, conveyor pass-throughs and production line inlets.
- Replacement or augmentation for traditional safety mats, light curtains or fixed guarding in flexible manufacturing setups.
- Troubleshooting Tips:
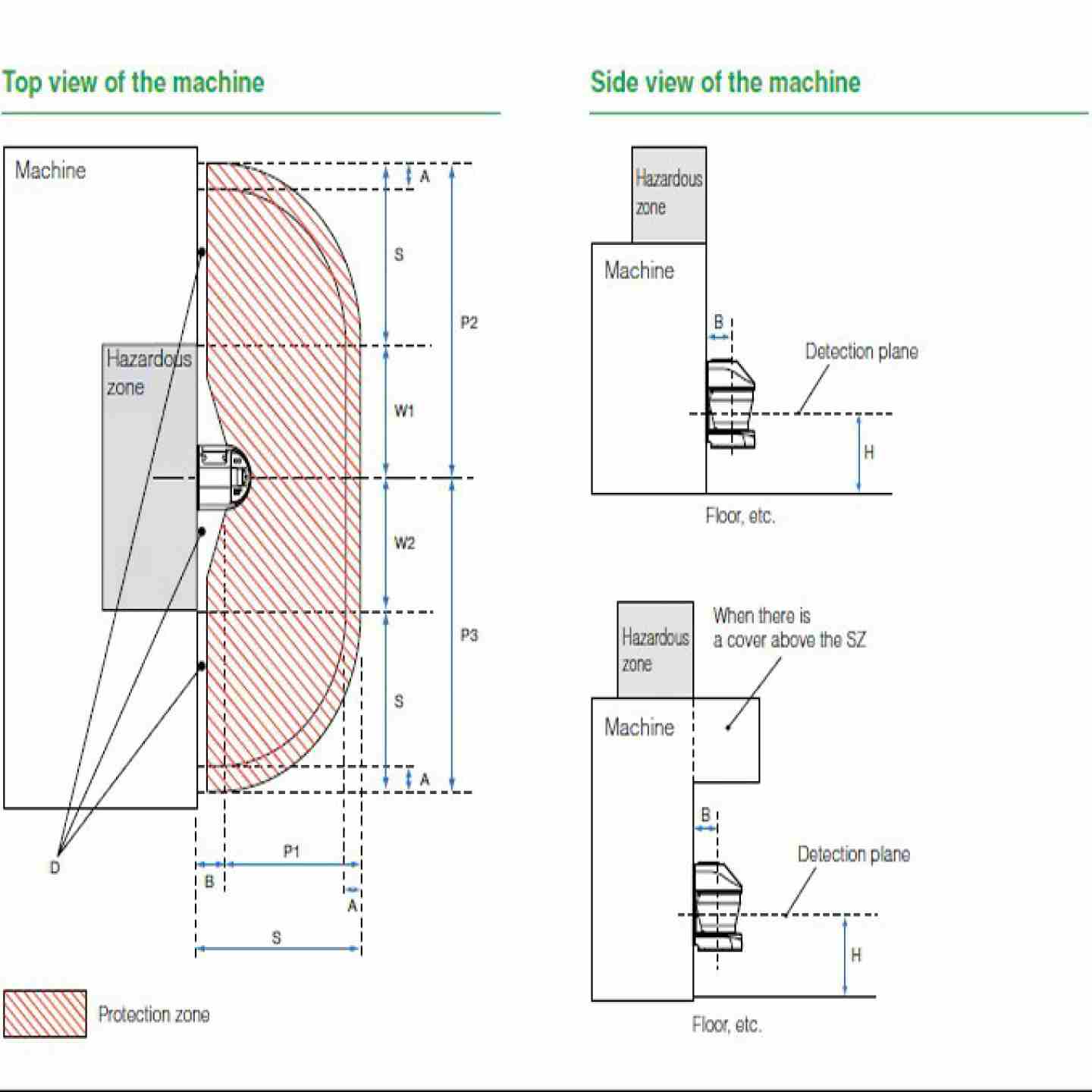
- Verify minimum safety distance: Ensure the scanner is installed at a distance from the hazard that complies with the required safety distance for the model (taking into account response time, beam spacing, and object size).
- Check mounting and alignment: Confirm that the scanner’s field of view covers the hazardous zone correctly and that the unit is firmly mounted (no drift or loosened brackets) so that its protective zone isn’t compromised.
- Inspect optical window and environment: Accumulated dust, oil mist, coolant spray or other contamination of the window may cause false trips or detection failures. Clean as required per the manual.
- Confirm correct wiring and outputs: Ensure the dual safety outputs (typically OSSD) and any auxiliary outputs are correctly wired into the safety PLC/relay system, and that the power supply meets the model’s specification.
- Check zone settings and bank switching: For scanners with multi-zone or bank-switching capability, verify each zone is configured properly and the bank switching logic is functioning (so that protective zones are truly protected).
- Review muting / blanking functions (if used): If the scanner is used in an application with material passing through the protective zone (e.g., AGV, conveyor), verify that muting or blanking configurations comply with the risk assessment and are operating as intended.
- Check for environmental interference / mutual interference: Situations such as direct sunlight, inverter lighting, or the use of multiple scanners in overlapping zones can cause malfunctions or degraded performance.
- Confirm firmware/configurator version: Use the manufacturer’s software (e.g., SZ-V Configurator) to check for configuration errors, communication issues (USB or Ethernet), and update firmware if necessary.
- Perform regular functional tests: After installation or maintenance, execute a full function test: introduce a known size object (per spec) into the protective zone, check that the machine stops, remove the object, reset the device, and verify normal operation.
- Check detection history/diagnostics: Use the built-in history or monitoring features (where supported) to review any error or alert states, false trips, or repeated warnings which may indicate root-cause issues.
- Verify installation in accordance with specification: Confirm the scanner isn’t used in an environment outside its rated specifications (temperature, humidity, vibration, contamination), and ensure it meets the required standards for the machine/application.