Presence Sensing Safety Devices
RFID safety switches (non-locking)
Robust, non-contact guarding with the tamper-resistant RFID interlock for modern machine safety.
High-integrity RFID interlock switch with inductive sensing, IP69K housing and Cat 4/SIL 3 capability for premium machine safeguarding.
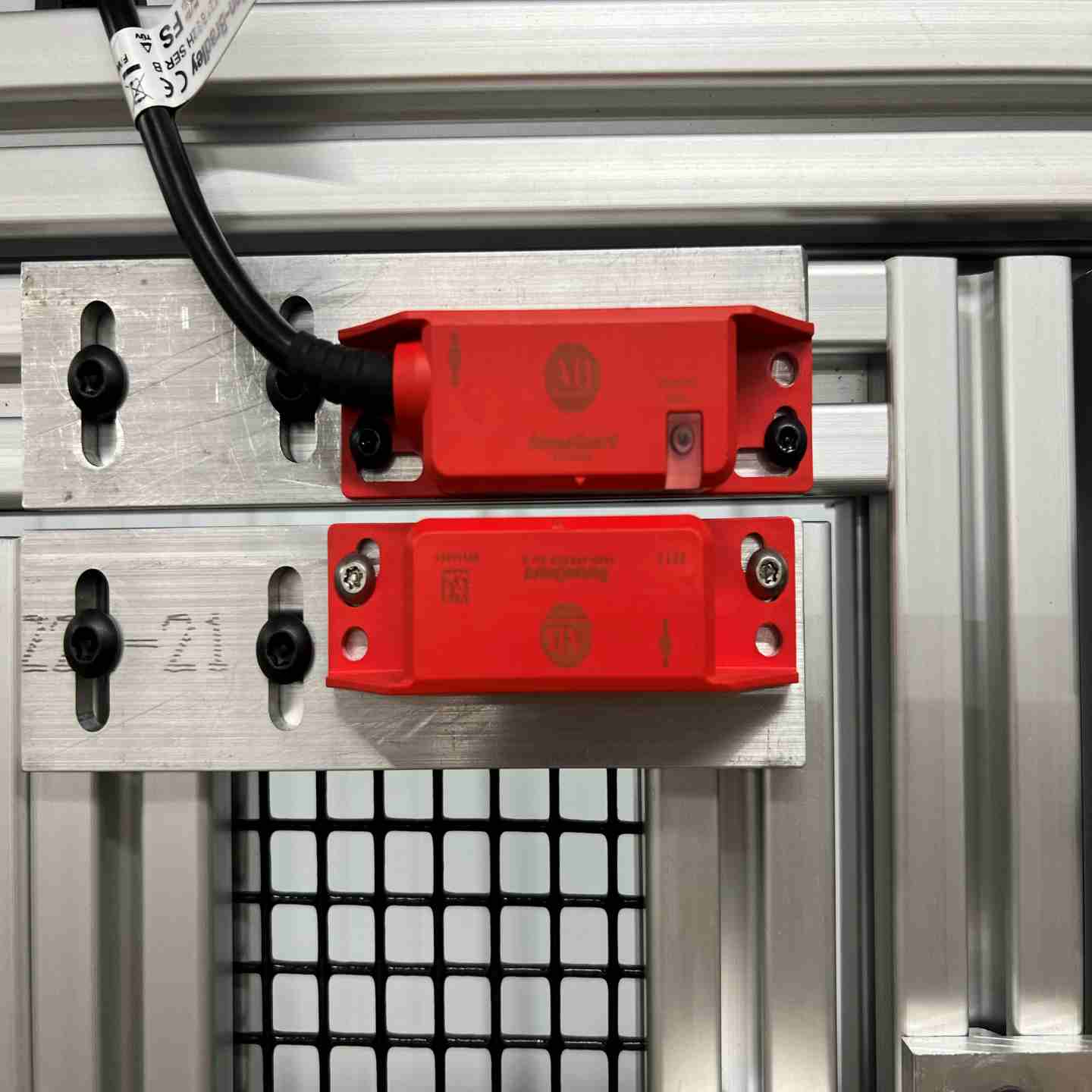
Non-locking RFID safety switches are non-contact, RFID-coded safety interlock devices designed to protect operators by monitoring the position of doors, gates, and machine guards. Using advanced RFID technology, SensaGuard switches provide high-tolerance misalignment, tamper-resistant operation, and Category 4 / PLe safety performance for demanding industrial environments. Ideal for guarding robotic cells, conveyors, packaging equipment, and automated machinery, these switches deliver reliable machine shutdown when a guard is opened—helping manufacturers meet OSHA, ANSI, and ISO safety requirements while improving uptime and reducing nuisance trips.
User-Friendly Design
- RFID and inductive sensing allow generous misalignment tolerance and long sensing range.
- LED diagnostics gives clear status and fault indication for fast troubleshooting.
- Compact barrel or flat-pack housings support flexible guard door styles and actuator types.
Flexible Mounting Options
- Available in plastic 18 mm or 30 mm barrels, stainless steel barrel and large flat-pack housings.
- Multiple actuator types including standard, magnetic-hold and integrated-latch versions to suit machine access points.
- IP66/IP67/IP69K rated versions for wash-down, high-moisture and harsh industrial environments.
Seamless System Integration
- Certified to IEC 60947-5-3, IEC 61508, ISO 13849 Cat 4/PL e, SIL 3 for highest-level safety performance.
- Supports series connection with other safety devices (light curtains, E-Stops, key-interlocks) without degrading PL/Cat rating.
- Compatible with standard M12 or quick-connect wiring, simplifying installation and maintenance.
RFID safety switches (non-locking)
Robust, non-contact guarding with the tamper-resistant RFID interlock for modern machine safety.
High-integrity RFID interlock switch with inductive sensing, IP69K housing and Cat 4/SIL 3 capability for premium machine safeguarding.
Non-locking RFID safety switches are non-contact, RFID-coded safety interlock devices designed to protect operators by monitoring the position of doors, gates, and machine guards. Using advanced RFID technology, SensaGuard switches provide high-tolerance misalignment, tamper-resistant operation, and Category 4 / PLe safety performance for demanding industrial environments. Ideal for guarding robotic cells, conveyors, packaging equipment, and automated machinery, these switches deliver reliable machine shutdown when a guard is opened—helping manufacturers meet OSHA, ANSI, and ISO safety requirements while improving uptime and reducing nuisance trips.
User-Friendly Design
- RFID and inductive sensing allow generous misalignment tolerance and long sensing range.
- LED diagnostics gives clear status and fault indication for fast troubleshooting.
- Compact barrel or flat-pack housings support flexible guard door styles and actuator types.
Flexible Mounting Options
- Available in plastic 18 mm or 30 mm barrels, stainless steel barrel and large flat-pack housings.
- Multiple actuator types including standard, magnetic-hold and integrated-latch versions to suit machine access points.
- IP66/IP67/IP69K rated versions for wash-down, high-moisture and harsh industrial environments.
Seamless System Integration
- Certified to IEC 60947-5-3, IEC 61508, ISO 13849 Cat 4/PL e, SIL 3 for highest-level safety performance.
- Supports series connection with other safety devices (light curtains, E-Stops, key-interlocks) without degrading PL/Cat rating.
- Compatible with standard M12 or quick-connect wiring, simplifying installation and maintenance.
- Assembly consists of:
- SensaGuard non-contact switch main unit and actuator.
- Mounting hardware for chosen housing type (barrel or flat-pack).
- Quick-connect cable or M12 cordset as selected.
- Product documentation: installation guide, safety data sheet, wiring instructions.
- Common uses include:
- Guard-door interlock for automated cells, robotic enclosures and packaging machines.
- Harsh-environment access control in food & beverage, pharma wash-down zones or heavy duty production lines.
- Machinery retrofit upgrades where higher safety integrity, non-contact sensing and improved diagnostics are required.
- Troubleshooting Tips:
- Test the actuator teaching cycle (if applicable): For unique-coded variants: ensure that the teach cycle completed correctly (actuator remained in sensing field for required time, LED sequence matched specs). If teach failed, the sensor may remain locked or not recognize any actuator.
- Inspect for mechanical issues / mounting hardware: Ensure the switch and actuator are mounted properly (tight bolts, no movement), that guard stops and guides are present (the device is not used as mechanical stop), and there’s no excessive vibration or shift that violates mounting specs.
- Check application environment for contamination/interference: Dirt, coolant, metal shavings, oil splatter around the sensor/actuator interface can impair detection or cause nuisance trips. Routine cleaning is recommended. Also ensure no external electromagnetic interference is present.
- Perform functional test of safety circuit: After installation or maintenance, perform a full functional test: open the guard; ensure outputs drop; attempt reset/operation with guard open — system must not allow restart until guard closed and system reset (if required). Refer to your safety control logic.
- Review diagnostic history / logged faults: If the unit has been indicating repeated fault/trip conditions, review the fault codes (via LED flashes or diagnostics module) and log them. Recurrent faults may point to root-cause such as actuator alignment drift, mounting degradation, or wiring loosening.
- Ensure correct zone sizing and guard arrangement: Use your machine risk assessment to confirm that the switch’s sensing range, actuator geometry, and guard door arrangement meet the required safe distances (per ISO 13855 / ISO 13849‑1). Incorrect guard design or door travel beyond the switch’s sensing window may undermine safety.
- Maintenance schedule: At regular intervals (e.g., quarterly/semi-annually depending on usage) inspect mounting hardware, clean optical/inductive surfaces, check actuator wear, retighten fasteners, validate wiring connectors for corrosion/looseness, and perform a full functional test.
Check power supply & wiring: Ensure the unit is powered at the correct 24 V DC (or per spec) and that wiring to the safety outputs (OSSDs) is correct and secure. Faulty wiring or voltage drop may cause the switch to fail to detect or drop outputs.- Check actuator alignment and sensing distance: The actuator must be within the sensing range and proper alignment relative to the sensor as per the mis-alignment curve. If the actuator is too far or angled incorrectly, the sensor may revert to “guard open” status.
- Verify unique-coded vs standard actuator matching: For unique-coded models, ensure you are using the correct actuator and that the “teach” process was completed. A mismatch or incomplete teaching will lead to no sensing or diagnostic fault.
- Monitor status/diagnostic LED indicators: The “Status/Diag” LED provides key diagnostic information:
- Solid green = safe/guard closed and outputs active. +1
- Red = not safe/guard open. Maxter Automatyka
- Flashing amber/green = actuator approaching max sensing distance (realignment required).
- Flashing red/green patterns = fault codes (learn failure, wrong actuator, exceeded learns) – use manual to decode.
- Check for short-circuit faults or output wiring faults: If a safety output is shorted (for example to 0 V or 24 V or another channel) the unit may shut off outputs or indicate fault. Confirm wiring integrity and that no channels are cross-shorted.