Presence Sensing Safety Devices
3d Safety Radars by Inxpect
Next-gen volumetric protection with the Inxpect Safety Radar
Adaptive 3D radar system for human-machine safeguarding — dust, light and debris resilient, configurable FOV up to 9 m.
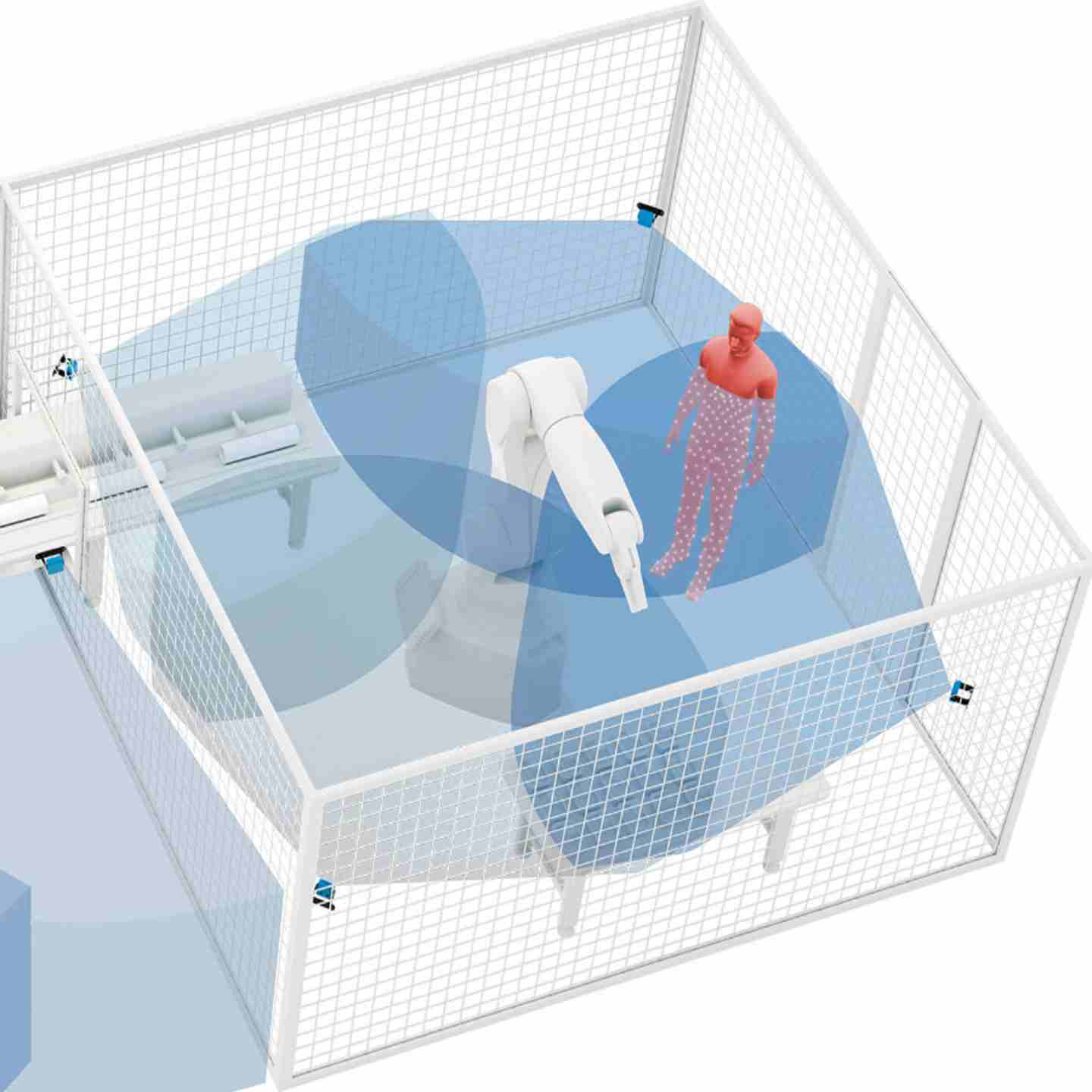
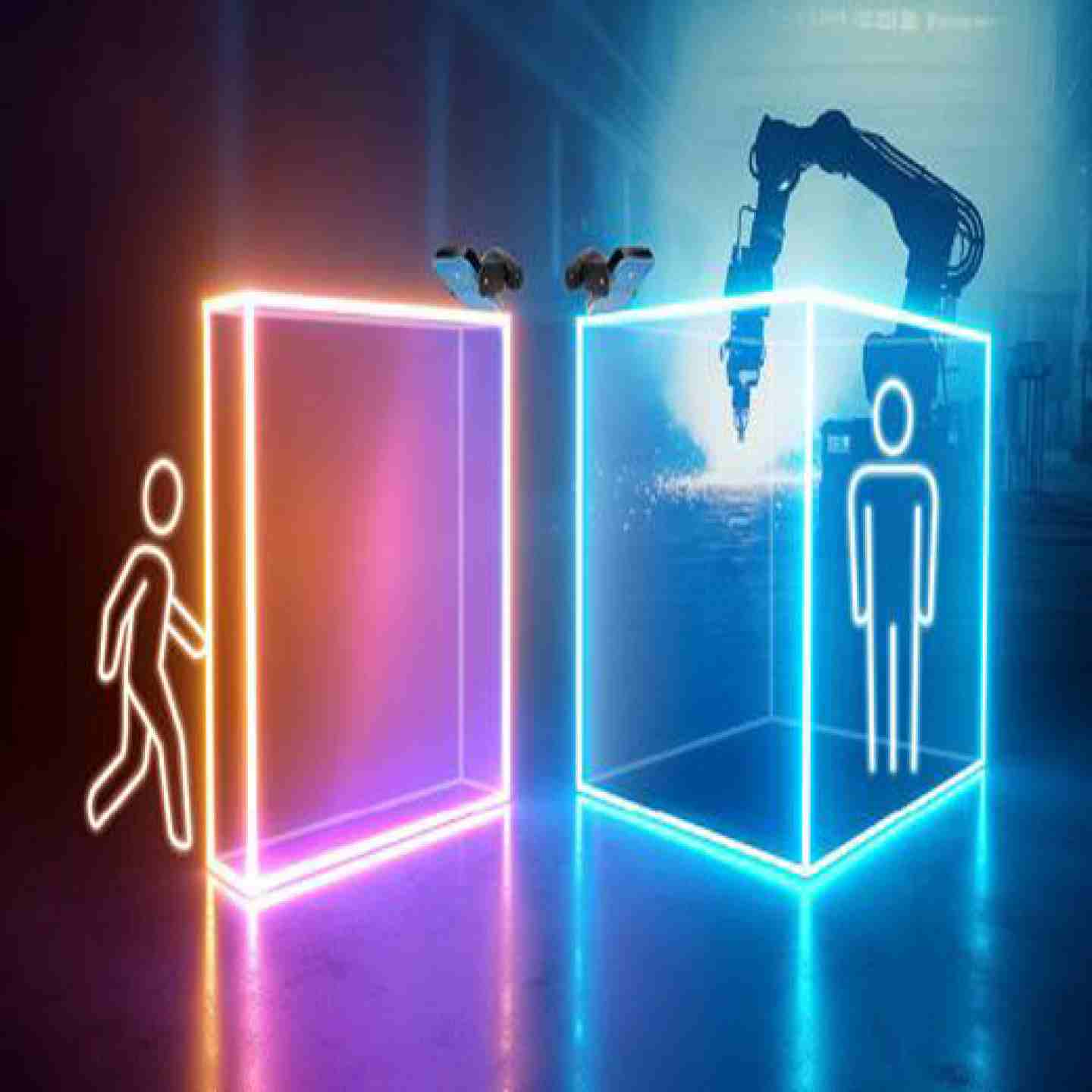
Inxpect 3D Safety Radars are volumetric, millimeter-wave radar sensors that create full three-dimensional safety zones around machines, mobile robots, AGVs and other dynamic industrial equipment. Unlike traditional planar safety devices (light curtains, laser scanners or mats), these radars deliver true volumetric protection—capable of detecting human presence even when an operator remains motionless. They are built to operate reliably in harsh environments, being immune to dust, smoke, debris, rain, splash and varying light conditions. Certified for functional safety (e.g., SIL2/PLd) and compliant with relevant safety standards, Inxpect radars support complex guarding concepts such as access prevention, machine restart protection and dynamic safety fields across mobile and fixed applications.
User-Friendly Design
- Intuitive 3D zonal configuration via software – warning & danger zones visually defined.
- Real-time dynamic modification of detection zones—useful for applications with moving machines or changing layouts.
- Minimal optical dependencies: radar based on FMCW technology, tolerates dust, smoke, lighting changes, splash.
Flexible Mounting Options
- Multiple Field of View (FOV) shapes (corridor, asymmetrical, cuboid) to match unique machine or mobile-platform layouts.
- Up to 9-metre range sensor variant supports large volume coverage for bigger cells or AGV/gantry systems.
- Indoor/outdoor IP67 rated systems—mountable on fixed guards, mobile robots, overhead cranes, or changing environments.
Seamless System Integration
- Certified to international safety standards: SIL2 / Performance Level d (PLd) / Category 3 — providing high integrity safety functions.
- System architecture supports up to six radar sensors per control unit, enabling scalable layouts and complex zone coverage.
- Compatible with modern fieldbus/ethernet safety protocols (ProfiSafe, etc.), and remote configuration via software or USB/ethernet.
3d Safety Radars by Inxpect
Next-gen volumetric protection with the Inxpect Safety Radar
Adaptive 3D radar system for human-machine safeguarding — dust, light and debris resilient, configurable FOV up to 9 m.
Inxpect 3D Safety Radars are volumetric, millimeter-wave radar sensors that create full three-dimensional safety zones around machines, mobile robots, AGVs and other dynamic industrial equipment. Unlike traditional planar safety devices (light curtains, laser scanners or mats), these radars deliver true volumetric protection—capable of detecting human presence even when an operator remains motionless. They are built to operate reliably in harsh environments, being immune to dust, smoke, debris, rain, splash and varying light conditions. Certified for functional safety (e.g., SIL2/PLd) and compliant with relevant safety standards, Inxpect radars support complex guarding concepts such as access prevention, machine restart protection and dynamic safety fields across mobile and fixed applications.
User-Friendly Design
- Intuitive 3D zonal configuration via software – warning & danger zones visually defined.
- Real-time dynamic modification of detection zones—useful for applications with moving machines or changing layouts.
- Minimal optical dependencies: radar based on FMCW technology, tolerates dust, smoke, lighting changes, splash.
Flexible Mounting Options
- Multiple Field of View (FOV) shapes (corridor, asymmetrical, cuboid) to match unique machine or mobile-platform layouts.
- Up to 9-metre range sensor variant supports large volume coverage for bigger cells or AGV/gantry systems.
- Indoor/outdoor IP67 rated systems—mountable on fixed guards, mobile robots, overhead cranes, or changing environments.
Seamless System Integration
- Certified to international safety standards: SIL2 / Performance Level d (PLd) / Category 3 — providing high integrity safety functions.
- System architecture supports up to six radar sensors per control unit, enabling scalable layouts and complex zone coverage.
- Compatible with modern fieldbus/ethernet safety protocols (ProfiSafe, etc.), and remote configuration via software or USB/ethernet.
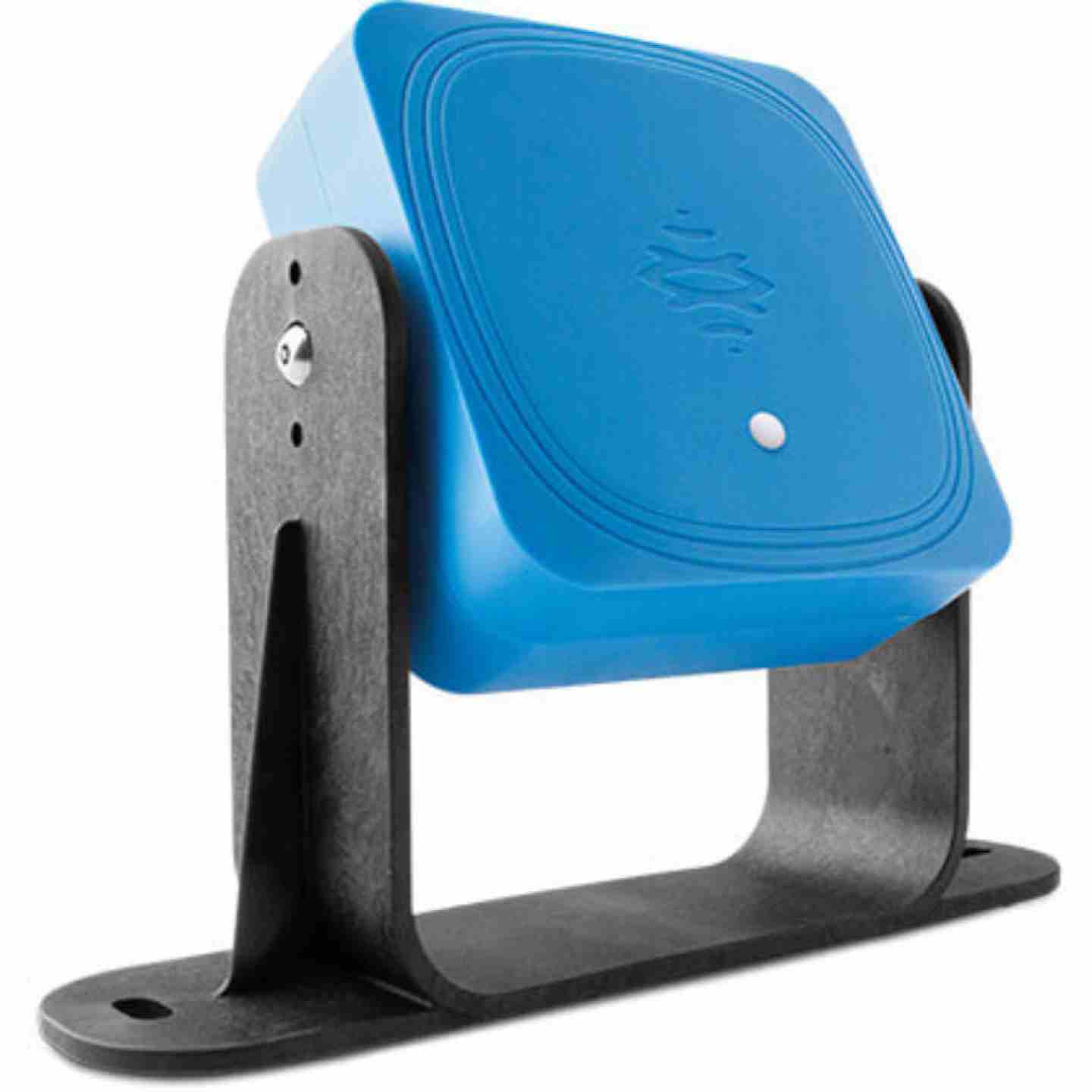
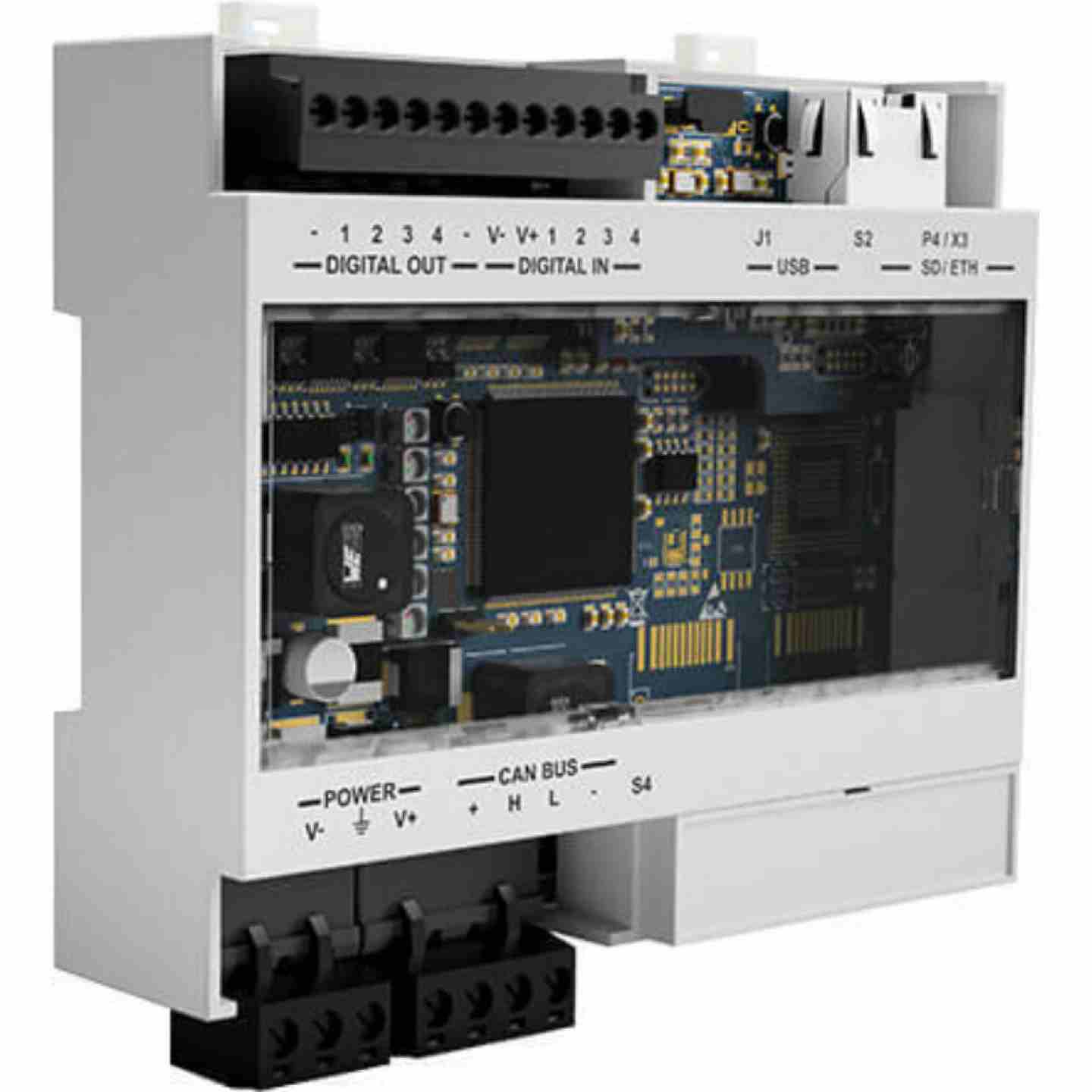
- Assembly consists of:
- Radar sensor main unit (e.g., S201A or similar from 200 Series)
- Safety control unit compatible with up to 6 sensors (bus/ethernet or digital I/O variant)
- Mounting bracket and hardware for selected installation orientation
- Configuration software (downloadable) + user manual/documentation
- Connection cable (sensor to control unit) — controller/safety relay and field-bus wiring sold separately
- Common uses include:
- Access protection and restart-prevention for robotic cells, automated machinery, AGVs and mobile platforms.
- Volumetric safeguarding in harsh industrial environments: where dust, debris, water spray or ambient light degrade optical sensors.
- Guarding large free-space zones where traditional light curtains/laser scanners are impractical (e.g., overhead gantry areas, loading bays).
- Troubleshooting Tips:
- Verify protective field layout & coverage: Confirm that the sensor’s configured detection zone (horizontal, vertical, and depth) fully covers the hazardous area as required by the risk assessment. Adjust angles, mounting height or coverage settings if people or equipment can enter the zone unseen.
- Check robustness in harsh environment: 3D radar sensors excel in dusty, smoky, or wet environments where optical sensors struggle. Ensure no heavy metallic reflectors or large moving machinery are creating interference/reflections that could degrade detection performance.
- Inspect mounting & alignment stability: Since volumetric scanning uses radio waves, ensure the sensor is mounted rigidly, vibrations are minimized and the sensor head is not shifted or rotated — misalignment can reduce detection reliability.
- Clean sensor window / housing & check for obstruction: While radar is more tolerant of contamination, build-up of heavy metal dust or welding spatter (especially near the sensor face) can still affect signal reflection or degrade performance. Remove deposits and verify clear line-of-sight where required.
- Validate reset, restart-prevention and access-detection logic: Many safety radar systems are used for restart prevention (i.e., machine cannot restart while a person is in the zone) and access detection. Test that the logic works as designed: after clearing the zone, the machine should not restart until sensor logic resets.
- Check diagnostics and status indicators: Use the manufacturer’s software or LEDs to review fault codes, sensor status, detection events and any muted or disabled zones. These diagnostics often give early warning of mis-configuration or drift.
- Assess potential mutual interference or overlapping fields: If multiple radar sensors or other RF/optical sensors operate nearby, check that fields do not overlap undesirably, causing ghost detection or dead zones. Test for unintended detection or failure to detect.
- Test functional performance after installation or maintenance: With power on and system operating: have a person enter the protective zone, verify machine stops or remains locked out; then clear the zone and verify reset and safe restart condition. Document the event and status.
- Schedule periodic inspections & calibration: Even though radar is robust, periodic verification of coverage, mounting, and detection performance is important. Check connector integrity, firmware/software updates, mounting hardware tightness, and environmental changes around the sensor.
- Ensure correct selection for application: Verify the sensor’s performance rating (e.g., PL d / SIL 2), sensing range, field shape, and certification suit the application (stationary machine, mobile robot, overhead crane, etc). Incorrect capability can lead to insufficient protection.